Getting to Know More About Recombinant Proteins
In this modern age of advanced medicine we have only scratched the surface of Recombinant Proteins. Though biotechnology has existed for more than a century now, it was only in the past decade or so when scientists started exploring genetic recombination and genetic engineering. Modern-day technologies have made it possible to manipulate genetic material to achieve desirable characteristics. Whether for medicinal, industrial, or agricultural purposes, genetic engineering has left a mark on these industries.
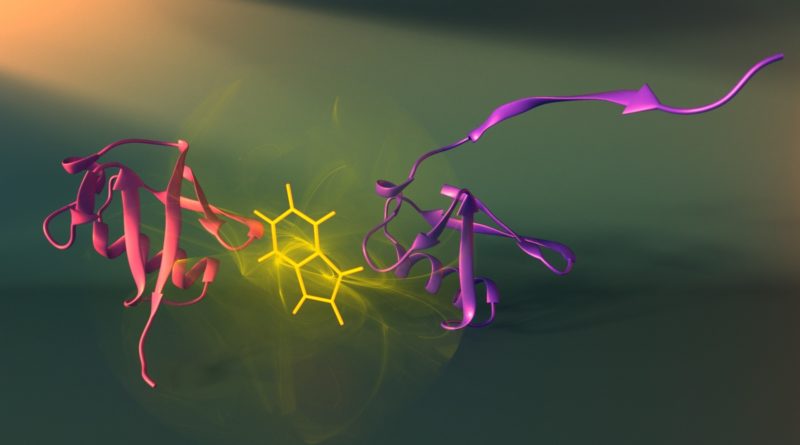
Recombinant DNA involves putting together DNA from different sources to create a new genetic combination and insert it into a host cell. This type of DNA can be modified to produce a recombinant protein, a manipulated form of a native protein that can trigger different cellular responses. Recombinant proteins are widely used in therapies, drugs, and biomedical research. Their extensive applications may explain why you may have seen recombinant proteins for sale to aid in research or the production of vaccines and hormones.
Since the discovery of recombinant proteins, scientists and researchers have been hard at work trying to uncover its potential. Here are some insights on these proteins and their contributions to various industries if you are curious to know more about them.
How Are Recombinant Proteins Made?
Recombinant proteins are made with recombinant DNA technologies to serve various purposes. They are essentially the product of translation when recombinant DNA is inserted into a target organism. Typically, the proteins are taken from organisms like bacteria, viruses, and Eukarya, and are then subject to rigorous testing and experimentation. Scientists will isolate the genetic material, make a clone, and find a suitable system to express it. The latter step is important to ensure the protein that is produced can perform its intended application.
With that said, researchers are constantly studying expression systems and looking for new technologies related to them. Some of the most common systems used today are expressions in E. coli, mammalian cells, yeast, insect cells, and in vitro. The expression system you choose will affect the type of proteins you produce. So, you have to determine the most suitable one to use carefully. It is why scientists typically start with a small-scale test. To see if the chosen system will generate their desired results.
Uses of Recombinant Proteins
If you have seen recombinant proteins for sale, you likely wondered what they are used for. First, recombinant proteins can contribute to research efforts to help scientists better understand how proteins interact with other cellular agents. Second, these proteins have been widely used for medicinal purposes. They serve as therapy for a range of diseases like hemophilia, anemia, and diabetes. These proteins can also be made into therapeutic proteins in the form of enzymes, antibodies, or hormones, to help protect an organism’s body.
Studies related to recombinant proteins continue to be published as scientists further investigate their potential in becoming treatments or vaccines. As such, it is no surprise that the recombinant protein industry has increased in the last 30 years. More and more proteins being developed for medicinal use.
These proteins may sound like a technical and complex topic, but they have proven to be milestone discoveries. They hold a large role in biotechnology and have led to significant contributions in medicine and scientific research. Given the applications that exist today, it is no question that recombinant proteins have more in store for the future.